 Alopex lagopus
Alopex lagopus
--------------
English: White fox
German: Polarfuchs
French: Renard blanc
Spanish: Zorro blanco
Distribution areas
------------------
The white fox can be found in polar
territories, in North Europe, and in North
America usually in areas above 60 degrees
of the northern latitude, and slightly
further south in Siberia . This animal has
two closely related varieties, the white
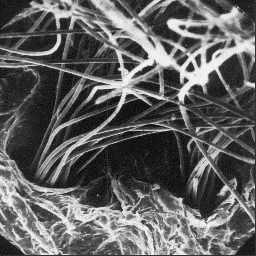
(polar) fox and the blue fox. The blue The surface structure
species is often raised on farms. of the skin, 200x
Description of the fur
----------------------
The skins are from 80 to 100 cm long, including the tail which is about
1/3rd of the total body length. The coat is very fine and dense. The summer
coat is brownish in colour but winter coat is usually white, with some
exceptions coloured in darker shades. The undercoat layer is always brown and
the individual fibres are curled.
|
|
 Alopex lagopus
Alopex lagopus
--------------
English: White fox
German: Polarfuchs
French: Renard blanc
Spanish: Zorro blanco
The guard hairs grow distinctively over
the undercoat, are fine and are curled in
the lower part and straight in the upper
part of the shaft. In comparison with the
red fox the skins are smaller, with shorter
legs and rounded ear lobes. The hair of the
white fox skin is dense, thick and has a
high felting ability. The length of the fine
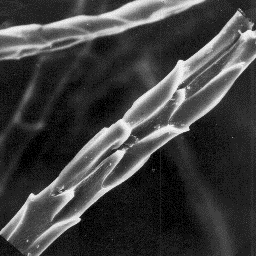
hair fibres is from 15 to 30 mm, the inter- The cuticular structure
mediate fibres are from 30 to 40 mm long and of the fine fibres, 1000x
the longest guard hairs are 75 to 85 mm
long.
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic structure of the skin surface appears slightly furrowed or
sometimes smooth. The upper part of the hair follicles is wide with straight
edges. The average follicle contains more than 10 hair shafts.
|
|
 Alopex lagopus
Alopex lagopus
--------------
English: White fox
German: Polarfuchs
French: Renard blanc
Spanish: Zorro blanco
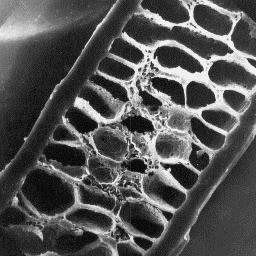
The fine fur fibres are from 5 to 7 µm
in diameter and the cross-sections are
circular in outline. The cuticular scales
have an indistinct shape in the proximity of
the skin surface but, along the shaft, the
scale pattern is expressive and is petal-
-like or flat-edge-shaped with sharpened
upper tips. The surface of the scales is
smooth or irregularly grooved and the Longitudinal section
margins are straight. In the cross-section, of a guard hair, 1000x
the area of the medulla occupies little more
than one half of the whole area but, at the bottom of the shaft, the fibres
are non-medullated. The medullar structure is unbroken longitudinally and is
of the central symmetrical-shaped cross-section. The overall medullar
structure is of the uniserial ladder type with the infilling substance having
a granular structure.
|
|
 Alopex lagopus
Alopex lagopus
--------------
English: White fox
German: Polarfuchs
French: Renard blanc
Spanish: Zorro blanco
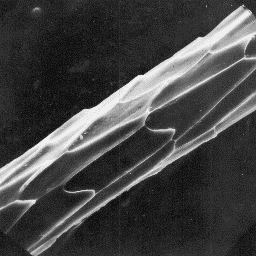
The intermediate fibres are, in the same
way as other hairs in the fox fur, curled
at the bottom part. The cross-sectional
outline is circular and measures from 15 to
25 µm in diameter. The cuticular scales are
flat edge-shaped with smooth scale surface
and scale margins. The medulla is wide with
a continual unbroken structure of symmet-
rical shape situated in the central axial The cuticular structure
part of the hair shaft. The overall struc- of an intermediate hair, 1000x
ture is of the uniserial ladder type with
a perforated sheet-like infilling substance.
The guard hairs have flattened upper parts with a diameter (major axis of
cross-section) reaching 50 or even 75 µm. The spear-shaped end is
approximately 5 mm long and its cross-section is often dumb-bell-shaped in
outline. The lower part of the hair shaft is circular. The cuticular scales
are of the rounded tile-like type, and are also comb-like in the lower part
of the shaft.
|
|
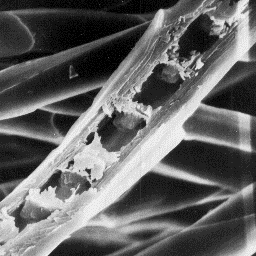 Alopex lagopus
Alopex lagopus
--------------
English: White fox
German: Polarfuchs
French: Renard blanc
Spanish: Zorro blanco
The scales have a smooth surface and
straight scale margins. The medulla of the
guard hairs is wide, unbroken and has
a central symmetrical-shaped cross-section.
In the upper part of the shaft, the overall
structure of the medulla is of the lattice
type, while, in the middle and lower parts
the medulla is of the uniserial ladder type.
The infilling substance of the medulla is of Longitudinal section
the perforated sheet-like structure. of a fine fur fibre, 2000x
Numerical code for white fox skin structure
-------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 1.3-2-3
Fine fur fibres: 1-10.11-1.3-1-2-1-1-2-6-5.7-15.25
Intermediate fibres: 1-10-1-1-2-1-1-8.1-2-15.25-30.45
Guard hairs: 2.8-6.3-1-1-2-1-1-8.1-2-50.75-45.85
|




