 Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
-----------------------------------
English: Wolf
German: Wolf
French: Loup
Spanish: Lobo
Distribution areas
------------------
The wolf lives in many parts of Europe,
in Asia and in North America. Now the
biggest population of wolves is found in
Siberia an Canada. This animal species has
a number of a different varieties according
to the geographic territory.
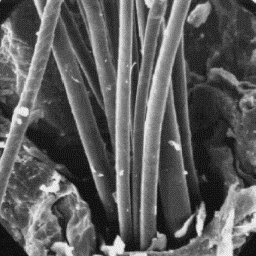
The surface structure
Description of the fur of the skin, 400x
----------------------
Continental wolves have skin from 80 to 125 cm long. The under-fur is very
apparent and blue grey in colour. The guard hairs are partially dark coloured
at the tips. The wolves from the North American territories have skins of up
to 180 cm long. The biggest are the wolves from arctic areas; they are white
in colour during the winter period. The wolves from woodland regions are
usually coloured gray; in the USA and Canada, some varieties are brown or
black in colour. In Asia, many varieties of wolves can be found, differing in
size and in colour of the skin.
|
|
 Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
-----------------------------------
English: Wolf
German: Wolf
French: Loup
Spanish: Lobo
Continental wolves have skin from 80 to
125 cm long. The under-fur is very apparent
and blue grey in colour. The guard hairs are
partially dark coloured at the tips. The
wolves from the North American territories
have skins of up to 180 cm long. The biggest
are the wolves from arctic areas; they are
white in colour during the winter period.
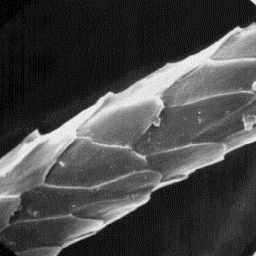
The wolves from woodland regions are usually The cuticular structure
coloured gray; in the USA and Canada, some of the fine fibres, 1000x
varieties are brown or black in colour. In
Asia, many varieties of wolves can be found, differing in size and in colour
of the skin. The coat of the wolf's skin is dense and soft with very fine
under-fur fibres and long coarse guard hairs. The underfur layer is about 12
to 20 mm thick; the length of the guard hairs is from 40 to 60 mm and, in some
parts of body, 100 mm or more.
|
|
 Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
-----------------------------------
English: Wolf
German: Wolf
French: Loup
Spanish: Lobo
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic appearance of the skin
surface is furrowed and the upper part of
the hair follicles is narrow with straight
edges. The follicles contain clusters of
ten or more hairs.
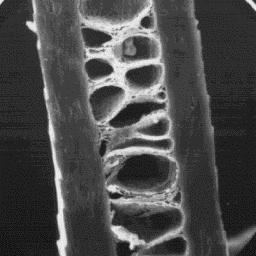
The fine fur fibres are of the circular Longitudinal section
cross-sectional outline and cuticular scale of an intermediate fibre, 1000x
at the bottom part of the shaft are of the
cornet-like type. In the middle and upper parts of the shaft, the fine fur
fibres have petal-like and flat edge-shaped scales. The surface of the
cuticular scales is smooth and the margins are straight. In the
cross-sectional view, the medulla occupies less than one half of the hair
shaft width. The medulla is unbroken longitudinally and central symmetrical
-shaped. The overall medullar structure is of the uniserial ladder type with a
foam-like and amorphous infilling substance. The diameter of the fine fibres
is in the range of 10 to 25 µm.
|
|
 Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
-----------------------------------
English: Wolf
German: Wolf
French: Loup
Spanish: Lobo
The intermediate fibres are circular in
cross-section with a diameter of 25 to
35 µm. The cuticular scales are of the comb-
-like or the flat edge-shaped type. At the
bottom of the hair shaft, proximal to the
skin surface, the cuticular scales are
sometimes also of the cornet-like type. The
scale surface is smooth and the margins are
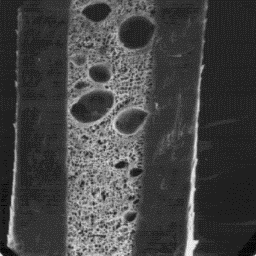
straight. The medulla is wide, unbroken and Longitudinal section
of the central symmetrical-shaped type. The of a guard hair, 2000x
overall medullar structure is of the lattice
spongelike type; at the bottom of the shaft, it is also of the uniserial
ladder type. The infilling material is foam-like or perforate sheet-like. The
guard hairs are straight and have a circular cross-sectional outline, 35 to
110 µm in diameter. The cuticle is composed of crenated tile-like scales with
smooth surfaces and rippled scale margins. The medulla is wide, unbroken and
central symmerrical-shaped. The overall medullar structure belongs to the
spongy-lattice type with a foam-like infilling substance.
|
|
 Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
Canis lupus (Continental varieties)
-----------------------------------
English: Wolf
German: Wolf
French: Loup
Spanish: Lobo
Longitudinal section
of a fine fur fibre, 600x
Numerical code for wolf skin structure
--------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-4-3
Fine fur fibres: 1-5.11-1-1-3-1-1-1-5.8-10.25-10.31
Intermediate fibres: 1-6.11-1-1-2-1-1-1.11-5.2-25.35-25.61
Guard hairs: 1-4-1-2-2-1-1-6-5-35.111-40.61
|




