 Capreolus capreolus
Capreolus capreolus
-------------------
English: Roe deer
German: Rehbock
French: Chevreuil
Spanish: Corzo
Distribution areas
------------------
Various species of roe live in the
woodland regions of Europe and Asia, except
in the most northern territories.
Description of the fur
----------------------
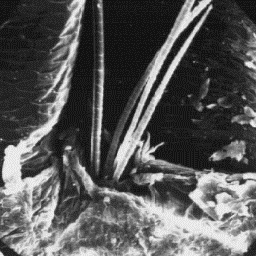
The roe skins are from 60 to 160 cm The surface structure
long; in the winter season, the coat is of the skin, 200x
coarse and the hairs breakable. The hair
fibres are grey-brown in colour at the bottom and light-grey in the upper
parts of the shaft. The summer skins are less dense, the fibres are stronger
and are red-brown in colour, and the under-fur layer is light-brown. The
individual hairs are straight; the guard hairs are from 35 to 55 mm long.
|
|
 Capreolus capreolus
Capreolus capreolus
-------------------
English: Roe deer
German: Rehbock
French: Chevreuil
Spanish: Corzo
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The structure of the winter skin is
quite different from that of the summer
one. In the winter coat, the prevailing fur
fibre type is the guard hair while, in
summer skins, the under-fur fibres prevail.
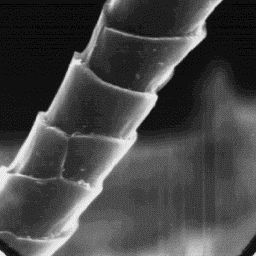
The structure of the fine fur fibres is
similar in both kinds of skin, but the The cuticular structure
guard hairs are very different. The of the fine fibres, 2000x
microscopic structure of the skin surface
is furrowed. The under-fur fibres grow in clusters from the narrow follicles
with straight edges. The guard hairs in the winter skin grow singly in the
follicles. The under-fur fine fibres are circular in cross-section with a
diameter of 12 to 20 µm. The cuticle consists of cornet-like scales with a
smooth surface and straight edges. These fine fur fibres are non-medullated.
|
|
 Capreolus capreolus
Capreolus capreolus
-------------------
English: Roe deer
German: Rehbock
French: Chevreuil
Spanish: Corzo
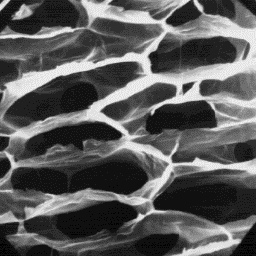
The intermediate fibres are present only
in the summer skin. Their diameter is from
30 to 80 µm and the cuticle is made from
the even tile-like scales. The cross-section
is circular. The width of the medulla is a
little under half of the shaft's width, so
it belongs to the narrow type. The scale
surface is irregularly grooved and the scale
margins are straight. The overall medullar Detailed structure
structure is of the lattice type and is of the medulla, 400x
unbroken and situated symmetrically in the
central axial area of the shaft. The medullar infilling substance is of the
needle-sheet-like structure.
The winter guard hairs are circular in cross-section with a diameter of
300 to 400 µm. In the upper part, the shafts are ellipsoidal in cross-
-sectional outline. The cuticle consists of even tile-like scales with both
scale surface and the scale margins being smooth. The medulla is of the
predominating type of structure.
|
|
 Capreolus capreolus
Capreolus capreolus
-------------------
English: Roe deer
German: Rehbock
French: Chevreuil
Spanish: Corzo
The cortex is not distinguishable. The
medullar structure is unbroken, central
symmetrical-shaped and of the lattice type.
The infilling substance is sheet-like. The
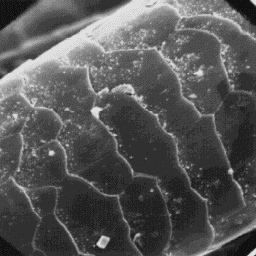
summer guard hairs are ellipsoidal in cross-
-section with a diameter of 90 to 110 µm.
The cuticular scales are of the even tile-
-like shape. The surface and the margins of
the scales are smooth. The medulla is wide, The cuticular structure
unbroken and symmetrically situated in the of an intermediate hair, 1000x
central axial part of the hair shaft. The
overall type of medulla belongs to the non-symmetrical non-uniform lattice
type, with a complex-sheet-like infilling substance.
|
|
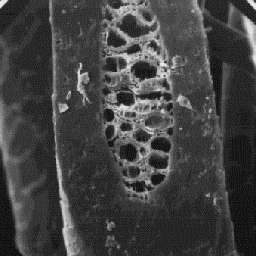 Capreolus capreolus
Capreolus capreolus
-------------------
English: Roe deer
German: Rehbock
French: Chevreuil
Spanish: Corzo
Transverse section
of a guard hair, 600x
Numerical code for roe deer skin structure
------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-1-3
Fine fur fibres: 1-5-1-1-4-0-0-0-0-12.21-8.31
Intermediate fibres: 1-2-1.3-1-3.2-1-1-8-3-30.81-30.51
Guard hairs: 2-2-1-1-2-1-1-10-4-90.111-30.51
|




