 Castor fiber
Castor fiber
------------
English: Beaver
German: Biber
French: Castor
Spanish: Castor
Distribution areas
------------------
In the past the beaver was found
throughout Europe, Asia and North America.
The European beaver is now very rare and is
protected by the state authorities. The
Canadian variety of beaver found in North
America has a larger population. The
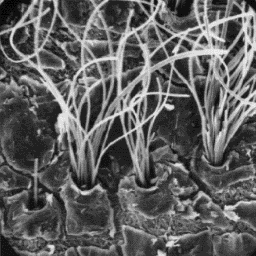
difference between the varieties is only The surface structure
mirror; the Canadian species has a narrower of the skin, 100x
head and its skin is darker in colour
Description of the fur
----------------------
The skin of beaver is from 50 to 100 cm long and light-brown in colour.
The guard hairs are straight, and are apparently longer than the fine
under-fur fibres. These coarse hairs are lustrous, bark-brown or red-brown in
colour and relatively scarce.
|
|
 Castor fiber
Castor fiber
------------
English: Beaver
German: Biber
French: Castor
Spanish: Castor
The guard hairs of the Canadian form of
beaver are dark-brown or black. The coat of
the beaver skin is relatively dense. The
length of the under-fur fibres is from 6 to
15 mm; the longest guard hairs are from 25
to 55 mm long.
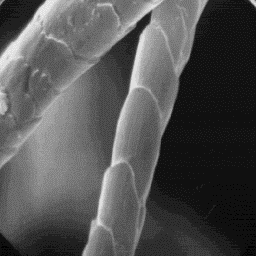
Structure of the hair
--------------------- The cuticular structure
The microscopic structure of the skin of the fine fibres, 2000x
surface is usually smooth; the hairs
follicles are wide with straight edges. The average follicle contains from 15
to 25 fibres in cluster.
The fine fur fibres have a circular cross-section with a diameter of 10 to
15 µm. The cuticular scales are of the cornet-like type with a smooth scale
surface and usually crenated scale margins. The fine fur fibres are non-
-medullated.
|
|
 Castor fiber
Castor fiber
------------
English: Beaver
German: Biber
French: Castor
Spanish: Castor
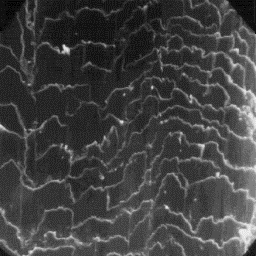
The intermediate fibres are very similar
in structure to the fine fibres but are
longer (from 15 to 30 mm), and their width
is from 20 to 25 µm. The cuticular scales
are cornet-like, smooth on the surface and
usually crenated at the margins. The
intermediate fibres are usually non-
-medullated.
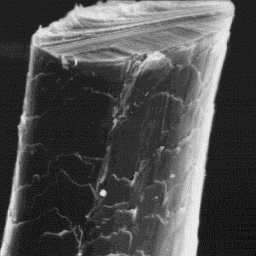
The cuticular structure
The guard hairs are circular in cross- of a guard hair, 1000x
-section in the lower part, and ellipsoidal
in the middle and upper parts of the shaft. The diameter of these fibres is
from 25 to 65 µm. The cuticle consists of even tile-like scales with a smooth
surface and rippled scale margins. The medullar structure is visible only in
come guard hairs; a large proportion of these hairs is non-medullated. The
medulla in the coarser guard hairs is wide, unbroken and central symmetrical-
-shaped. The medulla is of the lumpy type with an amorphous infilling
substance.
|
|
 Castor fiber
Castor fiber
------------
English: Beaver
German: Biber
French: Castor
Spanish: Castor
Transverse section
of a guard hair, 1000x
|
|
 Castor fiber
Castor fiber
------------
English: Beaver
German: Biber
French: Castor
Spanish: Castor
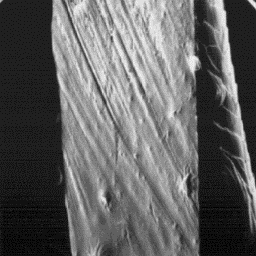
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 1000x
Numerical code for beaver skin structure
----------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 1-2-3
Fine fur fibres: 1-5-1-2-4-0-0-0-0-10.15-6.15
Intermediate fibres: 1-5-1-2-4-0-0-0-0-20.25-15.25
Guard hairs: 1.2-2-1-2-4.2-1-1-13-8-25.65-25.55
|




