 Leopardus pardalis
Leopardus pardalis
------------------
English: Ocelot
German: Ozelot
French: Ocelot
Spanish: Ocelote
Distribution areas
------------------
The ocelot and the similar species,
Leopardus tigrinus, are found in the
Southern and Middle American territories,
approximately between Peru and South Texas.
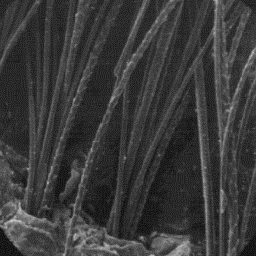
Description of the fur
---------------------- The surface structure
The skin is about 1 m long, covered by a of the skin, 200x
thin, dense coat, yellow-grey in colour
with dark spots which are circular or ellipsoidal in shape. The spots on the
back and on the top of head are stripe-like. The hair coat is about 12 to 18
mm thick, with a darker undercoat.
|
|
 Leopardus pardalis
Leopardus pardalis
------------------
English: Ocelot
German: Ozelot
French: Ocelot
Spanish: Ocelote
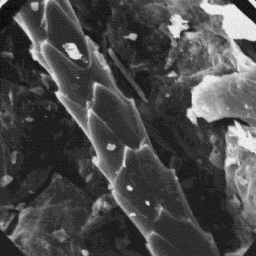
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface is furrowed and covered by narrow
follicles with straight upper edges.
Clusters of 4 to 15 hair fibres are found
in the follicles.
The fine fur fibres have a diameter of 9 The cuticular structure
to 18 µm. The cross-sectional outline is of the fine fibres, 1000x
circular, and the cuticular scales are
cornet-like or petal-like in shape. The surface of the cuticular scales is
smooth; the margins are straight. The medulla is narrow, unbroken and central
symmetrical-shaped in cross-section. The overall structure of the medulla
belongs to the uniserial ladder type with a foam-like or amorphous infilling
material.
|
|
 Leopardus pardalis
Leopardus pardalis
------------------
English: Ocelot
German: Ozelot
French: Ocelot
Spanish: Ocelote
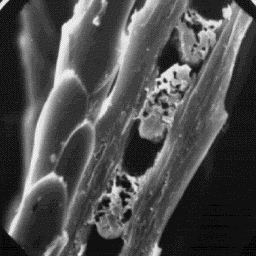
The intermediate fibres are from 20 to
30 µm in diameter. The cross-sectional
outline is circular but is ellipsoidal in
the upper part of the fibres. The cuticular
scales are petal-like in the lower parts,
and wavelike in the upper parts, of the
hair shafts. The scale surface is smooth
and the scale margins are straight. The
medulla is narrow, unbroken and central Longitudinal section
symmetrical-shaped in cross-section. The of a fine fur fibre, 2000x
overall structure of the medulla belongs to
the uniserial ladder type with an amorphous infilling
material.
The guard hairs have a diameter of 40 to 85 µm. The cross-sectional
outline is circular, and often is ellipsoidal in the upper part of the
fibres. The cuticular scales are even tile-like, smooth on the surface, and
rippled at the margins with numerous fine peaks on the outline.
|
|
 Leopardus pardalis
Leopardus pardalis
------------------
English: Ocelot
German: Ozelot
French: Ocelot
Spanish: Ocelote
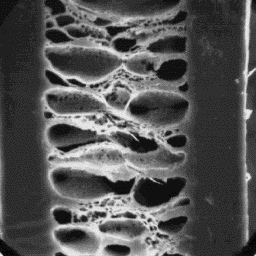
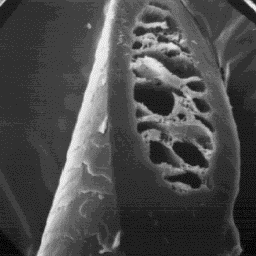
The medulla is wide, unbroken and sym-
metrically located in the central axial area
of the shaft. The overall structure of the
medulla belongs to the spongy-lattice-like
type with a foam-like infilling material.
Longitudinal section
of an intermediate fibre, 1000x
|
|
 Leopardus pardalis
Leopardus pardalis
------------------
English: Ocelot
German: Ozelot
French: Ocelot
Spanish: Ocelote
Transverse section
of an intermediate fibre, 1000x
Numerical code for ocelot skin structure
----------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-4-3
Fine fur fibres: 1-5.11-1-1-3-1-1-1-5.8-12.18-7.15
Intermediate fibres: 1.2-11.7-1-1-3-1-1-1-8-20.31-20.31
Guard hairs: 1.2-2-1-2-2-1-1-6-5-40.85-20.35
|




