 Panthera pardus
Panthera pardus
---------------
English: Leopard, panther
German: Leopard
French: Panthre
Spanish: Pantera
Distribution areas
------------------
About thriteen different leopard species
are known. They are found in Afrika or in
the Middle and Far East.
Description of the fur
----------------------
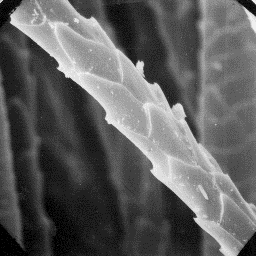
Leopard skins are from 120 to 160cm long, The surface structure
and somethimes even longer. The coat is of the skin, 200x
distinctly spotted. The hair is yellow-brown
in colour, darker on the back and lighter on the sides. The belly and insides
of the legs are white in colour. The upper parts of the body are covered by
round black spots with a diameter of between 8 and 45 mm. Some spots are
sickle-shaped. Some leopard skins are dark or even black in colour. The under-
coat i usually from 6 to 12mm thick and light-brown in color. The fine fur
fibres are moderately curled. The guard hairs are straight and usually from 12
to 18 mm long.
|
|
 Panthera pardus
Panthera pardus
---------------
English: Leopard, panther
German: Leopard
French: Panthre
Spanish: Pantera
Structure of the hair
---------------------
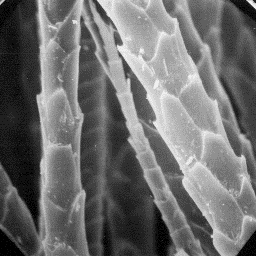
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface is furrowed; the hair follicles are
wide with sunken edges. The average follicle
contains from 8 to 16 hair shafts.
The fine fur fibres have a diameter of 12
to 25 µm and a circular cross-sectional The cuticular structure
outline. At the bottom of the shaft, the of the fine fibres, 1000x
cuticular scales are cornet-like but, in the
middle and upper parts, the scales are comb-like. The surface of the scales is
smooth and the margins are straight. These fine fibres are non-medullated.
The intermediate fibres are circular or ellipsoidal in cross-section with a
diameter of 25 to 40 µm. The cuticular scales are cornet-like at the bottom of
the shafts and comb-like in the middle and upper parts. The scale surface is
smooth and the margins are straight. The medula is narrow, unbroken and
situated symmetrically in the central axial part of the shaft.
|
|
 Panthera pardus
Panthera pardus
---------------
English: Leopard, panther
German: Leopard
French: Panthre
Spanish: Pantera
Some intermediate fibres are non medula-
ted. The overall medullar structure belong
to the spongly-lattice-like type with a
foam-like infilling substance.
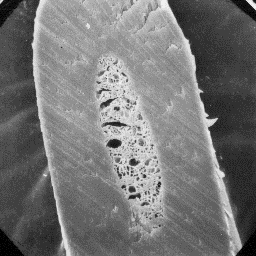
The guard hairs are from 50 to 100 µm in
diameter and the cross-sectional outline is
circular or ellipsoidal. The cuticular
scales are even tile-like shapped with a A group of the fine hairs,
smooth scale surface and straight margins. 1000x
The medullar column is narrow, unbroken and
central symmetrical-shaped. The overall medullar structure belongs to the
spongly-lattice-like type and the detailed structure of the infilling material
is foam-like.
|
|
 Panthera pardus
Panthera pardus
---------------
English: Leopard, panther
German: Leopard
French: Panthre
Spanish: Pantera
Transverse section
of a guard hair, 600x
|
|
 Panthera pardus
Panthera pardus
---------------
English: Leopard, panther
German: Leopard
French: Panthre
Spanish: Pantera
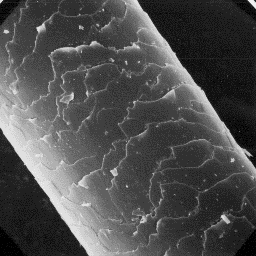
The cuticular structure
of a guard hair, 1000x
Numerical code for leopard skin structure
-----------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-1-3
Fine fur fibres: 1-5.6-1-1-4-0-0-0-0-12.25-6.25
Intermediate fibres: 2.1-6.5-1-1-3.4-1-1-6-5-25.40-12.25
Guard hairs: 2.1-2-1-1-3-1-1-6-5-50.100-15.30
|




