 Sus scrofa scrofa
Sus scrofa scrofa
-----------------
English: Wild boar
German: Wildschwein
French: Sanglier
Spanish: Jabalí
Distribution areas
------------------
The continental form of the wild boar
can be found in the wooded areas of Europe
and Asia. In other parts oft the world,
about nine different varieties of the
species are known.
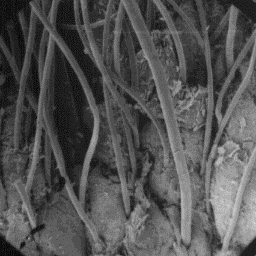
Description of the fur The surface structure
---------------------- of the skin, 40x
The skins are from 80 to 160 cm long.
The corium layer is thick and hard. The undercoat is white or light in colour
and more apparent in the winter coat. The prevailing fibres are coarse hairs
(bristles) with straight shafts, which are grey-black or brown-black in
colour.
|
|
 Sus scrofa scrofa
Sus scrofa scrofa
-----------------
English: Wild boar
German: Wildschwein
French: Sanglier
Spanish: Jabalí
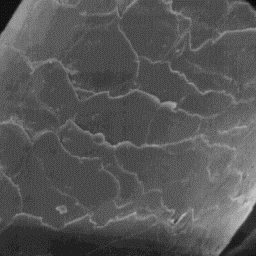
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic skin surface is
furrowed. The hair follicles are narrow
with straight edges. The average follicle
contains only one hair shaft.
The fine fur fibres have a circular
cross-sectional outline measuring from 30 The cuticular structure
to 60 µm in diameter. The cuticle is of an intermediate hair, 1000x
covered by crenated tile-like scales with a
smooth surface and rippled scale margins. The medullar column is not
present.
|
|
 Sus scrofa scrofa
Sus scrofa scrofa
-----------------
English: Wild boar
German: Wildschwein
French: Sanglier
Spanish: Jabalí
The intermediate fibres are circular in
cross-sectional outline at the bottom of
the shaft, and ellipsoidal in the middle
and upper parts. The diameter is from 60 to
100 µm. The cuticular scales are crenated
tile-like in shape with a smooth surface
and rippled scale margins. These inter-
mediate fibres are usually non-medullated.
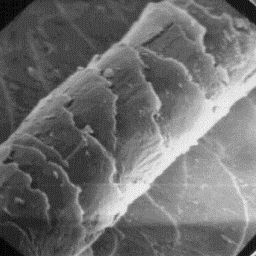
The cuticular structure
The guard hairs are either circular or of the fine fibres, 2000x
ellipsoidal in cross-sectional outline with
a diameter of 60 to 250 µm. The cuticular scales are crenated tile-like in
shape, the scale surface is smooth and the margins are rippled. The medullar
column is very variable; in some hairs, it is not present; in others, it is
narrow; and, in most coarse hairs it is wide. The wide medulla is usually
unbroken but the narrow medulla is often longitudinally broken. The outline of
the medullar cross-section is central symmetrical-shaped and the overall
structure belongs to the spongy-cortex-like type with either a foam-like or
amorphous infilling substance.
|
|
 Sus scrofa scrofa
Sus scrofa scrofa
-----------------
English: Wild boar
German: Wildschwein
French: Sanglier
Spanish: Jabalí
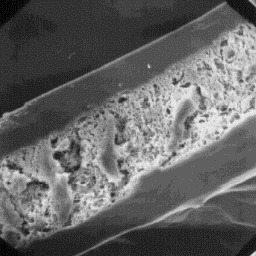
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 400x
|
|
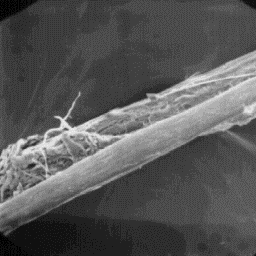 Sus scrofa scrofa
Sus scrofa scrofa
-----------------
English: Wild boar
German: Wildschwein
French: Sanglier
Spanish: Jabalí
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 200x
Numerical code for wild boar skin structure
-------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-4-1
Fine fur fibres: 1-4-1-2-4-0-0-0-0-30.61-8.35
Intermediate fibres: 2.1-4-1-2-4-0-0-0-0-60.101-25.41
Guard hairs: 2.1-4-1-2-2.3-1.2-1-7-5.8-60.251-25.55
|




