 Acinonyx jubatus
Acinonyx jubatus
----------------
English: Cheetah
German: Gepard
French: Quepard
Spanish: Leopardo cazador
Distribution areas
------------------
There are two varieties subspecies of the
cheetah, one of which lives in Africa
the other in West Asia. The Indian variety
of the cheetah (Acinonyx jubatus venaticus)
is lighter in colour and has more distinct
hair.
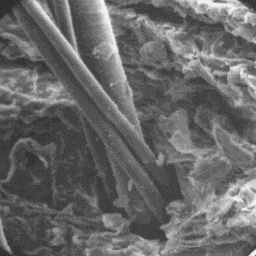
The surface structure
Description of the fur of the skin, 300x
----------------------
The coat is coarse and consists of yellow-grey fibres, in some places it is
spotted grey or black. The skins are from 120 to 140 cm long and the tail is
about 75 cm long. The belly part is white in the african variety, but spotted
in the asiatic kind. The colour of the undercoat is similar to the other parts
of the coat. The thickness of the coat is from 20 to 40 mm and even more in
the mane.
|
|
 Acinonyx jubatus
Acinonyx jubatus
----------------
English: Cheetah
German: Gepard
French: Quepard
Spanish: Leopardo cazador
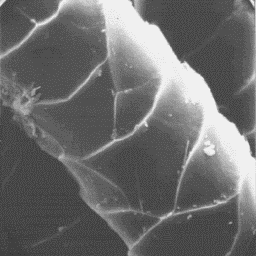
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface is furrowed; the hair follicles are
narrow with straight edges. The average
follicle contains 3 to 8 hairs, only some
guard hairs emerge from follicle singly.
The fine fur fibres are circular in The cuticular structure
cross-section with a diameter of from 10 to of the fine fibres, 2000x
25 µm. The cuticular scales are cornet-like
with a fine, regularly-grooved surface and straight scale margins. The medulla
is wide, with the exception of the bottom part of the fibres (when it is
omitted) and is longitudinally unbroken and central symmetrical-shaped in
cross-section. The overall structure of the medulla is sponge-cortex-like with
an amorphous or foam-like infilling substance.
|
|
 Acinonyx jubatus
Acinonyx jubatus
----------------
English: Cheetah
German: Gepard
French: Quepard
Spanish: Leopardo cazador
The intermediate fibres are circular or
elliptic in cross-section, with a diameter
of 30 to 55 µm. The cuticular scales are
even, tile-like with a smooth or regularly
-grooved surface and straight scale margins.
The medulla is wide, unbroken and central
symmetrical-shaped in cross-section. The
overall structure of the medulla is the
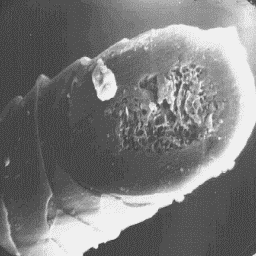
sponge-cortex-like type with an amorphous or Transverse section
foam-like infilling substance. of a fine fur fibre, 2000x
The guard hairs are circular at the bottom, and elliptic in the middle
and upper parts of the shaft. The diameter is from 60 to 75 µm. The cuticular
scales are crenated tile-like with a smooth scale surface and straight scale
margins. The medulla is wide, unbroken and central symmetrical-shaped
in cross-section. The overall medullary pattern is again on the sponge-cortex
-like type with an amorphous or foam-like infilling material.
|
|
 Acinonyx jubatus
Acinonyx jubatus
----------------
English: Cheetah
German: Gepard
French: Quepard
Spanish: Leopardo cazador
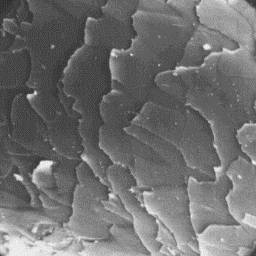
The cuticular structure
of a guard hair, 2000x
|
|
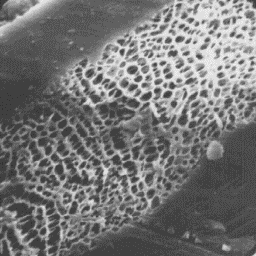 Acinonyx jubatus
Acinonyx jubatus
----------------
English: Cheetah
German: Gepard
French: Quepard
Spanish: Leopardo cazador
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 2000x
Numerical code for cheetah skin surface
---------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-4-3
Fine fur fibres: 1-5-2-1-2-1-1-7-5.8-10.25-5.25
Intermediate fibres: 1.2-2-1.2-1-2-1-1-7-5.8-30.55-20.31
Guard hairs: 1.2-4-1-1-2-1-1-7-5.8-60.75-30.45
|




