 Capra sibirica
Capra sibirica
--------------
English: Siberian ibex
German: Sibirisher steinbock
French: Bouquetin de siberie
Spanish: Cabra mont‚s de siberia
Distribution areas
------------------
The siberian ibex is found in Siberia.
Description of the fur
----------------------
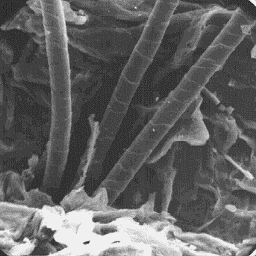
The skin of mature animal is 110 to 150
cm long. In the winter season the coat is
white-grey in colour, the summer coats are The surface structure
brown. The colour is uniform over the whole of the skin, 600x
body.
|
|
 Capra sibirica
Capra sibirica
--------------
English: Siberian ibex
German: Sibirisher steinbock
French: Bouquetin de siberie
Spanish: Cabra mont‚s de siberia
Structure of the hair
---------------------
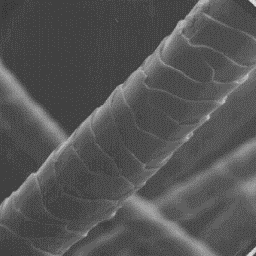
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface appears furrowed. The openings of
the hair follicles are wide with straight
edges. The hairs usually emerge from
follicles in groups; only coarse guard
hairs occur singly.
The cuticular structure
The fine fur fibres are 8 to 12 µm in of the fine fibres, 1000x
diameter and their cross-sections are
circular or elliptical. The cuticular scale pattern is of the cornet-like
type, with both the surface and the margins of the scale being smooth. The
fine hairs have a central symmetrical type of medulla, which is wide,
unbroken and of the lattice-sponge-like type. The medullar infilling
substance is either of the foam-like or amorphous structure.
|
|
 Capra sibirica
Capra sibirica
--------------
English: Siberian ibex
German: Sibirisher steinbock
French: Bouquetin de siberie
Spanish: Cabra mont‚s de siberia
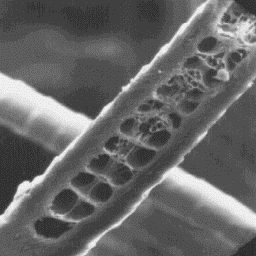
The intermediate fibres are circular in
the bottom part, but elliptical in other
parts of the shaft. Their width is 20 to 40
µm. The cuticular scales are of the even,
tile-like type, smooth on the surface and
usually with straight margins. The medulla
is wide, unbroken and central
symmetrical-shaped. The medulla is of
lattice type with an amorphous infilling Longitudinal section
substance. of an intermediate fibre, 1000x
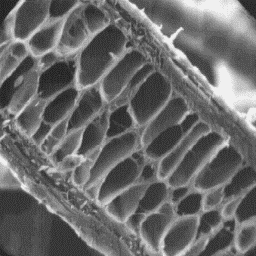
The guard hairs are elliptical in cross-sectional outline, and 20 to 60 µm
in diameter. The cuticular-scale pattern is of an even, tile-like type with a
smooth scale surface and straight scale margins. The medulla is the
predominating structure in the winter-coat guard hairs, and wide in the
summer one. The overall structure is of the central symmetrical-shaped,
unbroken lattice type. The medullary infilling substance is of the sheet-like
structure.
|
|
 Capra sibirica
Capra sibirica
--------------
English: Siberian ibex
German: Sibirisher steinbock
French: Bouquetin de siberie
Spanish: Cabra mont‚s de siberia
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 1000x
|
|
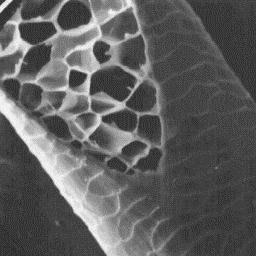 Capra sibirica
Capra sibirica
--------------
English: Siberian ibex
German: Sibirisher steinbock
French: Bouquetin de siberie
Spanish: Cabra mont‚s de siberia
Transverse section
of a guard hair, 400x
Numerical code for siberian ibex skin structure
-----------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-2-3
Fine fur fibres: 1.2-5-1-1-2-1-1-11-5.8-8.12-10.28
Intermediate fibres: 1.2-2-1-1-2-1-1-8-8-20.41-30.45
Guard hairs: 2-2-1-1-1-1-1.2-8-1-35.61-40.61
|




