 Cavia aperea
Cavia aperea
------------
English: Guinea-pig
German: Herschweinchen, aperea
French: Cobaye sauvage
Spanish: Conejillo de Indias
Distribution areas
------------------
The guinea-pig is found mainly in areas
of South and Central America, where it
occurs in the wild, but this animal is now
also domesticated and bred in many parts of
the world.
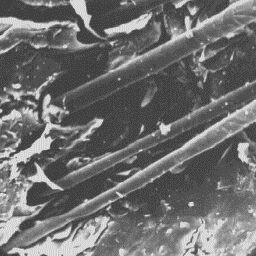
Description of the fur The surface structure
---------------------- of the skin, 300x
The skins are from 10 to 18 cm long. The
coat is relatively coarse and brown with white spots in colour. The hairs are
straight, 15 to 20 mm long.
|
|
 Cavia aperea
Cavia aperea
------------
English: Guinea-pig
German: Herschweinchen, aperea
French: Cobaye sauvage
Spanish: Conejillo de Indias
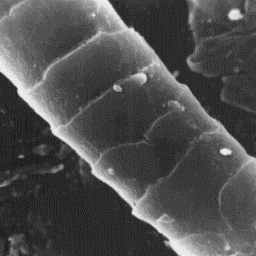
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface is relatively smooth, covered by a
thick epidermal layer. The upper opening of
the follicles is wide and is approximately
at the same level as the skin surface. The
average follicle contains only one hair
shaft. The cuticular structure
of the fine fibres, 2000x
The fine fur fibres have a diameter of
15 to 30 µm. The cross-sectional outline is circular at the bottom, and
elliptical in the upper parts of the shaft. The cuticular scales are of the
flat edge-shaped type, only at the bottom they are cornet-like. Over most of
the surface a tiny, regularly grooved pattern is visible. The scale margins
are straight. The medulla is wide, unbroken and central symmetrical shaped in
cross-section. The overall medullary structure is of the uniserial ladder
type with the broken patches in a longitudinal direction. The infilling
substance of the medulla is amorphous.
|
|
 Cavia aperea
Cavia aperea
------------
English: Guinea-pig
German: Herschweinchen, aperea
French: Cobaye sauvage
Spanish: Conejillo de Indias
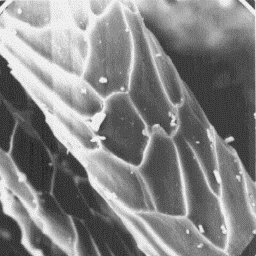
The intermediate fibres have a diameter
between 25 and 50 µm. The cross-section is
circular at the bottom and elliptical in
the other parts of the shaft. The cuticular
scales are of the even, tile-like type, or
sometimes flat edge-shaped. The scale
surface is grooved and scale margins are
straight. The medulla is wide, unbroken and
central symmetrical-shaped. The overall The cuticular structure
structure is of the lattice type with an of an intermediate hair, 1000x
amorphous infilling substance.
The guard hairs are circular of elliptical in cross-section with diameters
of 40 to 65 µm. The cuticular scales are even, tile-like with the scale
surface grooved in the lower part of the shaft and, elsewhere, it is smooth.
The scale margins are straight. The medulla is wide, unbroken and central
symmetrical-shaped in cross-section. The medullar structure is of the lattice
type with an amorphous infilling substance.
|
|
 Cavia aperea
Cavia aperea
------------
English: Guinea-pig
German: Herschweinchen, aperea
French: Cobaye sauvage
Spanish: Conejillo de Indias
The cuticular structure
of a guard hair, 300x
|
|
 Cavia aperea
Cavia aperea
------------
English: Guinea-pig
German: Herschweinchen, aperea
French: Cobaye sauvage
Spanish: Conejillo de Indias
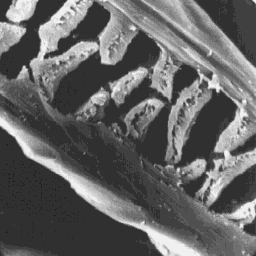
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 1500x
Numerical code for guinea-pig skin structure
--------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 1-2-1
Fine fur fibres: 1.2-10.5-2-1-2-1-1-3-8-15.31-7.25
Intermediate fibres: 2.1-2.11-2-1-2-1-1-8-8-25.51-12.19
Guard hairs: 2.1-2-2.1-1-2-1-1-8-8-40.65-20
|




