 Cervus elaphus wapiti
Cervus elaphus wapiti
---------------------
English: Wapiti
German: Rothirsch
French: Cerf rouge
Spanish: Ciervo comun
Distribution areas
------------------
The wapiti deer is found in North
America, but the species is similar to the
deer found in Europe and Asia. About twenty
deer species are known.
Description of the fur
---------------------- The surface structure
Deer skins are from 165 to 250 cm long, of the skin, 1000x
with a tail about 15 to 15 cm long. The
coat is thick, containing coarse and easily-broken fibres, especially in the
winter season. Long coarse fibres are slightly curled along the length. The
coat is grey or brown-grey in colour.
|
|
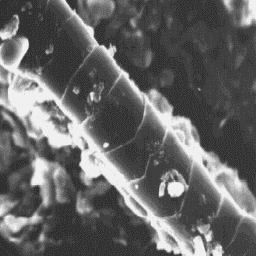 Cervus elaphus wapiti
Cervus elaphus wapiti
---------------------
English: Wapiti
German: Rothirsch
French: Cerf rouge
Spanish: Ciervo comun
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic skin surface structure
is furrowed. The hair follicles are narrow
and with straight edges. The average
follicle contains only one fibre.
The fine fur fibres are 12 to 25 µm in
diameter. The cross-section is circular and The cuticular structure
the cuticular scales are cornet-like with a of the fine fibres, 2000x
smooth scale surface and straight scale
margins The hairs of the fine type are
non-medullated.
|
|
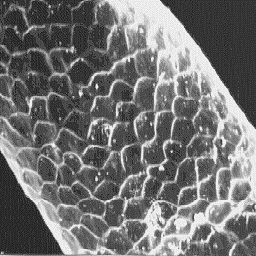 Cervus elaphus wapiti
Cervus elaphus wapiti
---------------------
English: Wapiti
German: Rothirsch
French: Cerf rouge
Spanish: Ciervo comun
The intermediate fibres and guard hairs
are very similar in the shape and differ
only in the diameter.
In the lower part of the shaft, near to
the skin surface, the cross-sectional
outline is circular, but most of the shaft
has an elliptical cross-section. The
diameter is in the range of 120 to 340 µm. The cuticular structure
The cuticular scale are tile-like in the of a guard hair, 200x
lower part, and mosaic-like in the upper
part of the hair shaft. The scale surface is smooth and the scale margins are
straight. These coarse fibres are medullated with the medulla of the
prevailing type, the cortex structure between the medulla and the cuticle
cannot be distinguished. The medullary column is unbroken and situated
symmetrically in the central axial area of the shaft. The overall medullary
structure is of the symmetrical non-uniform lattice type. The infilling
medullary substance is of the sheet-like structure.
|
|
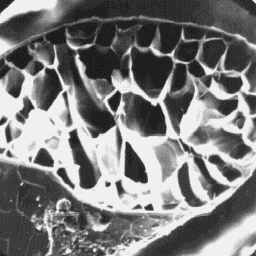 Cervus elaphus wapiti
Cervus elaphus wapiti
---------------------
English: Wapiti
German: Rothirsch
French: Cerf rouge
Spanish: Ciervo comun
Transverse section
of a guard hair, 300x
|
|
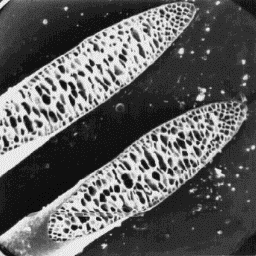 Cervus elaphus wapiti
Cervus elaphus wapiti
---------------------
English: Wapiti
German: Rothirsch
French: Cerf rouge
Spanish: Ciervo comun
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 60x
Numerical code for wapiti skin structure
----------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-4-1
Fine fur fibres: 1-5-1-1-4-0-0-0-0-12.25-5.21
Intermediate fibres: 2.1-1.2-1-1-1-1-1-9-1-120.221-30.55
Guard hairs: 2.1-1.2-1-1-1-1-1-9-1-220.341-40.58
|




