 Marmota bobac
Marmota bobac
-------------
English: Bobac marmot
German: Bobak
French: Marmotte bobac
Spanish: Marmota de Siberia
Distribution areas
------------------
The bobac marmot lives in the prairie
areas of Middle Asia, mostly in Mongolia. In
Europe, three varieties of a similar species
Marmota marmota, can be found. Different
varieties are found in other parts of the
world. The total number of known species of
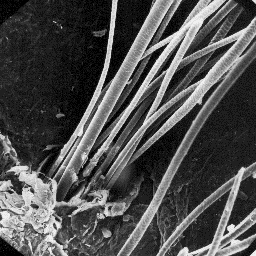
marmot is eleven. The surface structure
of the skin, 100x
Description of the fur
----------------------
The skin of bobac marmot is about 50 cm long and, in some cases, up to
70cm. The upper part of the coat is light-brown in colour. The tips of the
guard hairs are dark; the undercoat layer is also dark-brown. The thickness of
the undercoat layer is about 10 to 18 mm; the length of the coarse hairs is
from 15 to 30 mm, and in some cases, up to 40 mm.
|
|
 Marmota bobac
Marmota bobac
-------------
English: Bobac marmot
German: Bobak
French: Marmotte bobac
Spanish: Marmota de Siberia
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface appears moderately furrowed; the
hair follicles are narrow with raised edges,
and contain clusters of hair shafts usually
with between 15 and 25 individual fibres.
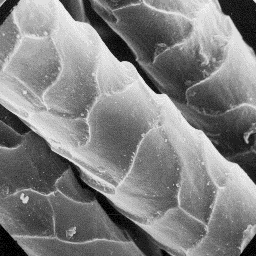
The fine fur fibres have a diameter of 15 The cuticular structure
to 25 µm. The cross-sectionaloutline is of the fine fibres, 2000x
circular at the bottom, and ellipsoidal at
the top, of the shaft. The cuticular scales are rounded tile-like in shape
with a grooved scale surface and straight scale margins. The medulla is
narrow, unbroken and central symmetrical-shaped in cross-section. The overall
medullar structure belongs to the uniserial ladder type with a perforated
sheet-like infilling substance.
|
|
 Marmota bobac
Marmota bobac
-------------
English: Bobac marmot
German: Bobak
French: Marmotte bobac
Spanish: Marmota de Siberia
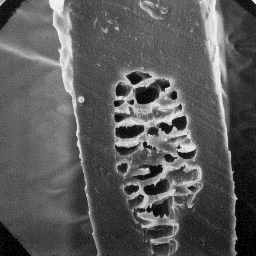
The intermediate fibres have a diameter
of between 30 and 50 µm. The cross-section
is circular at the bottom, and ellipsoidal
in the other parts, of the hair shaft. The
cuticular scales are even tile-like or
rounded tile-like in shape. The scale
surface is finely grooved and the scale
margins are straight.
Transverse section
The medullar column is narrow, unbroken of an intermediate fibre, 600x
and central symmetrical-shaped in cross-
section. The overall structure of the medulla belongs to the uniserial ladder
type or to the lattice type with a perforated sheet-like infilling material.
The guard hairs have a diameter of 50 to 90 µm and their cross-section is
usually ellipsoidal in outline. The cuticular scales are even tile-like or
rounded tile like, with an irregularly grooved surface and straight scale
margins. The medulla is wide, unbroken and central symmetrical-shaped in
cross-section.
|
|
 Marmota bobac
Marmota bobac
-------------
English: Bobac marmot
German: Bobak
French: Marmotte bobac
Spanish: Marmota de Siberia
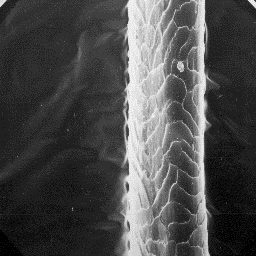
The overall structure belongs to the
lattice type with a complex-sheet-like
infilling substance.
The cuticular structure
of an intermediate hair, 400x
|
|
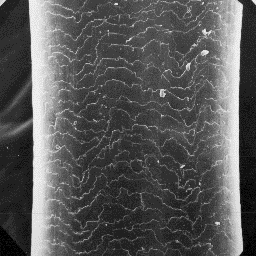 Marmota bobac
Marmota bobac
-------------
English: Bobac marmot
German: Bobak
French: Marmotte bobac
Spanish: Marmota de Siberia
The cuticular structure
of a guard hair, 400x
Numerical code for bobac marmot skin structure
----------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-5-3
Fine fur fibres: 2.1-3-2-1-3-1-1-1-2-15.25-10.18
Intermediate fibres: 2.1-2.3-2-1-3-1-1-8.1-2-30.50-15.20
Guard hairs: 2-2.3-3-1-2-1-1-8-4-50.90-15.40
|




