 Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
-----------------------------
English: Sheep
German: Hausschaf
French: Mouton
Spanish: Ovejas
The sheep is one of the oldest domes-
ticated animals and, today, many varieties
are bred in all the inhabited continents.
The species can be classified into three
groups according to the wool quality: the
fine wool type, the semi-fine wool type and
the coarse wool type. Zoologically, the
sheep could be classified into four groups.
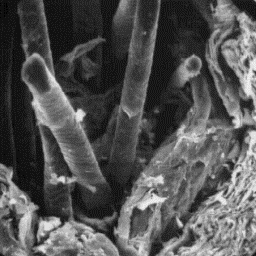
In the first group are the fatty-tailed The surface structure
sheep, yielding high quality Persian furs, of the skin, 200x
for example Kara-kul, Balcanian, Moldavian,
Bagdad type and others. In the second group are the wide- backed sheep, with
semi-Persian wool, for example, the Astrakhan, Tibetian, Indian, Pakistan and
Afghanistan breeds. The third group covers the short-tailed breeds with coarse
wool. These sheep are the older and, today industrially less important types
and, for fur purposes, only lamb skins are used. The last group are the
thin-tailed sheep, with a fine wool coat, which are the most important in the
wool industry. The main representatives of this group are the merino species
and similar fine wool-coated types.
|
|
 Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
-----------------------------
English: Sheep
German: Hausschaf
French: Mouton
Spanish: Ovejas
Distribution areas
------------------
The cigaja lamb skin belongs to the
semi-fine wool sheep which originated in
the areas around the river Danube and is in
the territories around the Black Sea and in
the entire Balkan peninsula.
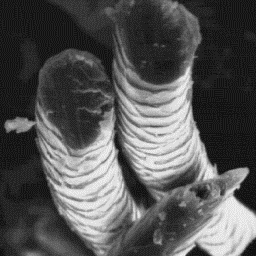
Description of the fur Transverse section
---------------------- of a fine fur fibre, 600x
The skins have an area of 60 to 400 cmý
and the weight is usually in the range of 0.2 to 1 kg. The coat is white or
light in colour. The smaller ones are sometimes darker, brown, grey or black
in colour. The hair fibres are only moderately curled; the appearance is
lustrous and elastic. The thickness of the coat is between 15 and 30 mm.
|
|
 Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
-----------------------------
English: Sheep
German: Hausschaf
French: Mouton
Spanish: Ovejas
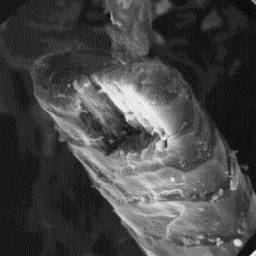
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic surface structure of the
skin is furrowed, consisting of narrow hair
follicles with straight edges. The average
follicle contains only one hair shaft.
The fine fur fibres have a circular
cross-sectional outline and measure from 20 Transverse section
to 30 µm in diameter. The cuticular scales of an intermediate fibre, 1000x
are either cornet-like or even tile-like in
shape with a smooth scale surface and straight margins. These fibres are
non-medullated.
|
|
 Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
-----------------------------
English: Sheep
German: Hausschaf
French: Mouton
Spanish: Ovejas
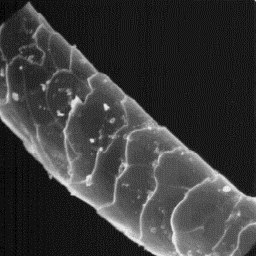
The intermediate fibres are ellipsoidal
and, at the bottom of the shaft, often
circular in cross-section with a diameter
of 30 to 40 µm. The cuticle is covered by
even tile-like scales with a smooth or
non-regular grooved surface and straight,
sometimes rippled scale margins.
The guard hairs are circular or The cuticular structure
ellipsoidal in cross-sectional outline with of the fine fibres, 1000x
a diameter of about 40 to 80 µm. The
cuticular scales are even tile-like with a non-regular grooved surface and
straight, sometimes rippled, scale margins. As in the other fibre types,
these coarse fibres are also non-medullated in the majority of cases.
|
|
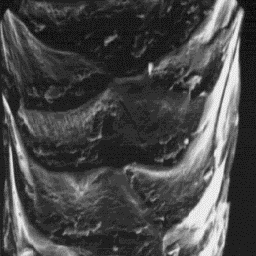 Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
Ovis aries - Cigaja lamb skin
-----------------------------
English: Sheep
German: Hausschaf
French: Mouton
Spanish: Ovejas
The cuticular structure
of an intermediate hair, 2000x
Numerical code for cigaja lamb skin structure
---------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-4-1
Fine fur fibres: 1-5.2-1-1-4-0-0-0-0-20.31-8.25
Intermediate fibres: 2.1-2-1.3-1-4-0-0-0-0-30.41-15.35
Guard hairs: 2.1-2-3-1.2-4-0-0-0-0-40.81-25.45
|




