 Panthera pardus japonensis
Panthera pardus japonensis
--------------------------
English: Chinese leopard
German: Chinese leopard
French: L‚opard de chine
Spanish: Leopard de china
Distribution areas
------------------
The chinese leopard lives in the
woodland regions of South-East Asia. This
variety is similar to other leopard
varieties, living in Africa and other parts
of Asia.
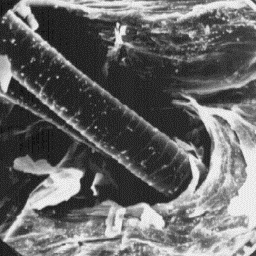
Description of the fur The surface structure
---------------------- of the skin, 200x
The skins are from 95 to 170 cm long;
the tail is between 60 and 100 cm. In contrast to the common leopard, these
skins have a thicker coat, the hair fibres are up to 50 mm long and the tail
is covered by longer hairs. The hair fibres are grey-yellow or red-brown in
colour. The most characteristic feature are the black spots, often arranged
into elliptical patterns, which cover the upper part of the body. The coarse
hairs are straight, but the fine fur fibres are moderately curled.
|
|
 Panthera pardus japonensis
Panthera pardus japonensis
--------------------------
English: Chinese leopard
German: Chinese leopard
French: L‚opard de chine
Spanish: Leopard de china
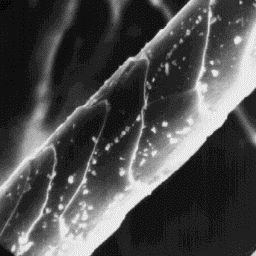
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic structure of the skin
surface is usually regularly grooved. The
hair follicles are narrow with raised
edges. The average follicle contains two
hair shafts.
The fine fur fibres are elliptical in The cuticular structure
cross-section with a diameter of 15 to 25 of the fine fibres, 600x
µm. The cuticular scales are of the
cornet-like type and also of the flat edge-shaped structure. The cuticular
scales are finely grooved over the surface; the scale margins are straight.
The medulla is narrow, unbroken and central symmetrical-shaped in
cross-section. The medullary structure is of the non-regular type with an
amorphous or foam-like infilling substance.
|
|
 Panthera pardus japonensis
Panthera pardus japonensis
--------------------------
English: Chinese leopard
German: Chinese leopard
French: L‚opard de chine
Spanish: Leopard de china
The intermediate fibres are elliptical
in cross-section and the diameter of the
fibres is from 35 to 75 µm. The cuticular
scales are even, tile-like with a smooth
surface and straight scale margins. The
medulla is narrow, unbroken and central
symmetrical-shaped in cross-section. This
medulla is of the sponge-lattice-like type
with a foam-like structure of the infilling The cuticular structure
material. of the fine fibres, 2000x
The guard hairs are elliptical in cross-section. These hairs are from 75
to 115 µm in diameter. The cuticular scales are even, tile-like or, in the
upper parts of the shaft, the crenated, tile-like. The cuticular surface is
smooth and scale margins are straight. The medulla is wide, unbroken and
central symmetrical shaped. The overall structure of the medulla is the
sponge-lattice-like. The infilling substance is foam-like.
|
|
 Panthera pardus japonensis
Panthera pardus japonensis
--------------------------
English: Chinese leopard
German: Chinese leopard
French: L‚opard de chine
Spanish: Leopard de china
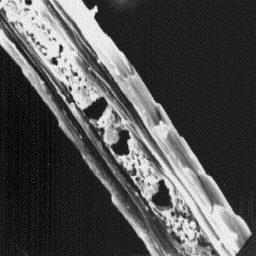
Longitudinal section
of an intermediate fibre, 2000x
|
|
 Panthera pardus japonensis
Panthera pardus japonensis
--------------------------
English: Chinese leopard
German: Chinese leopard
French: L‚opard de chine
Spanish: Leopard de china
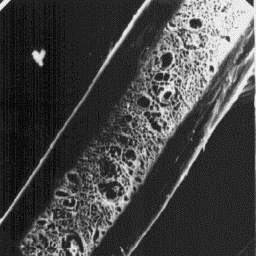
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 600x
Numerical code for chinese leopard skin structure
-------------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 2-5-2
Fine fur fibres: 2.1-5.11-2-1-3-1-1-16-5.8-15.25-7.14
Intermediate fibres: 2-2-1-1-3-1-1-6-5-35.75-15.35
Guard hairs: 2-2.4-1-1-2-1-1-6-5-75.115-20.51
|




