 Rupicapra rupicapra
Rupicapra rupicapra
-------------------
English: Chamois
German: Gemse
French: Chamois
Spanish: Gamuza
Distribution areas
------------------
Chamois live in the mountainous regions
of the Europe and Asia Minor.
Description of the fur
----------------------
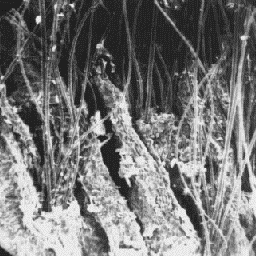
The skins are from 120 to 136 cm long
and the tail about 5 to 8 cm. The hair coat The surface structure
is soft and up to 50 mm in thickness. The of the skin, 60x
hair shafts are straight, only the fine fur
fibres are moderately curled. The underfur layer is not distinguished. The
coat is dark-brown with a contrasting black and white mask on the face. In
the winter the coat is black-brown in colour.
|
|
 Rupicapra rupicapra
Rupicapra rupicapra
-------------------
English: Chamois
German: Gemse
French: Chamois
Spanish: Gamuza
Structure of the hair
---------------------
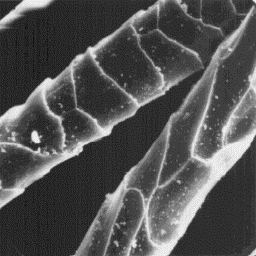
The microscopic structure of the skin is
usually furrowed, but sometimes also the
surface is covered by parallel grooves. The
hair follicles are narrow with straight
edges, and contain a cluster of the fibres.
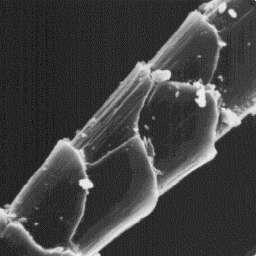
The fine fur fibres have a circular The cuticular structure
cross-section with a diameter of 8 to 14 of the fine fibres, 1500x
µm. The cuticular scales are of the
cornet-like type with a non-regular grooved surface and straight scale
margins. These fine fibres are non-medullated.
|
|
 Rupicapra rupicapra
Rupicapra rupicapra
-------------------
English: Chamois
German: Gemse
French: Chamois
Spanish: Gamuza
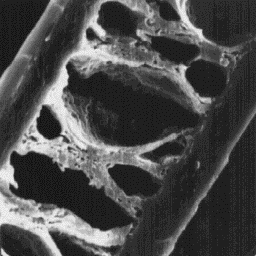
The intermediate fibres are circular or
elliptical in cross-section. The diameter
of these fibres is from 20 to 35 µm. The
cuticle consists of even tile-like scales
with a smooth surface and straight scale
margins. The medulla is wide, unbroken and
central symmetrical-shaped in the
cross-section. The medullary structure is
of the spongelike, or sometimes The cuticular structure
sponge-lattice-like type. The infilling of the fine fibres, 4000x
substance belongs to the foam-like
structure.
The guard hairs are oval in cross-section and their width is from 35 to 50
µm. The cuticular scales are even tile-like in lower half of the shafts, and
the crenated tile-like in upper part, of the shafts. The scale surface is
smooth and margins are straight. The medulla is wide, unbroken and central
symmetrical-shaped in cross-sectional outline. The medulla belongs to the
sponge-lattice-like type, or sometimes the spongelike type. The infilling
substance is foam-like.
|
|
 Rupicapra rupicapra
Rupicapra rupicapra
-------------------
English: Chamois
German: Gemse
French: Chamois
Spanish: Gamuza
Longitudinal section
of an intermediate fibre, 2000x
|
|
 Rupicapra rupicapra
Rupicapra rupicapra
-------------------
English: Chamois
German: Gemse
French: Chamois
Spanish: Gamuza
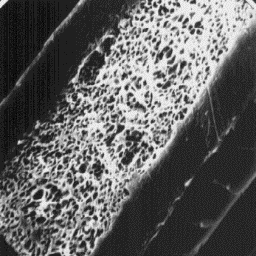
Longitudinal section
of a guard hair, 2000x
Numerical code for chamois skin structure
-----------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3.2-4-3
Fine fur fibres: 1-5-3-1-4-0-0-0-0-8.14-15.31
Intermediate fibres: 1.2-2-1-1-2-1-1-5.6-5-20.35-20.41
Guard hairs: 2-2.4-1-1.2-2-1-1-6.5-5-35.51-40.51
|




