 Sciurus vulgaris
Sciurus vulgaris
----------------
English: Squirrel
German: Eichhorn
French: Ecureuil
Spanish: Ardilla
Distribution areas
------------------
The squirrel can be found throughout
Europe and in wooded areas of Asia and
North America. In the other continents,
about eleven different varieties of the
squirrel species are known.
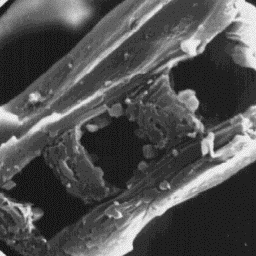
Description of the fur Longitudinal section
---------------------- of a fine fur fibre, 4000x
The skin of the common squirrel is from
20 to 30 cm long, and the tail is nearly the same length. The fur coat is
red-brown and, in some cases, dark-brown or even black in colour. The belly
is much lighter in colour, often white. The squirrels from North European
territories and from Siberia have a grey winter coat but the summer coat is
not different from that of the common squirrels. The coat is dense and fine,
with an undercoat of about 8 to 12 mm thick and coarse hairs up to 20 mm long.
|
|
 Sciurus vulgaris
Sciurus vulgaris
----------------
English: Squirrel
German: Eichhorn
French: Ecureuil
Spanish: Ardilla
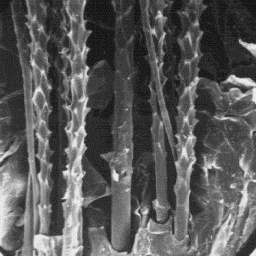
Structure of the hair
---------------------
The microscopic skin surface is furrowed;
the hair follicles are narrow with straight
edges and usually contain only one hair
shaft. The follicles are often in groups of
3 or 5 and are close together.
The fine fur fibres have an aster-like The surface structure
cross-section with the exception of the of the skin, 400x
lowest part of the shaft, where the outline
is circular. The diameter of these fibres is from 6 to 12 µm. The cuticular
scales are of the raised edge-shaped type. The scale surface is smooth and the
margins are straight. The medulla is wide, unbroken and central symmetrical
-shaped. The overall medullar structure belongs to the uniserial ladder type
with either a granular or amorphous infilling substance.
|
|
 Sciurus vulgaris
Sciurus vulgaris
----------------
English: Squirrel
German: Eichhorn
French: Ecureuil
Spanish: Ardilla
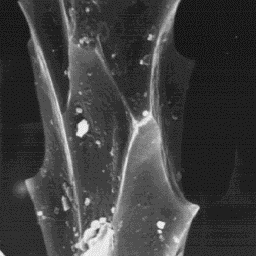
The intermediate fibres are circular at
the bottom, and ellipsoidal in the middle
and upper parts, of the shaft. The diameter
is between 25 and 50 µm. The cuticle is
covered by comb-like scales with a smooth
surface and straight scale margins. The
medullar column is wide, unbroken and
central symmetrical-shaped. The overall
medullar structure is of the uniserial The cuticular structure
ladder type with a granular or amorphous of the fine fibres, 3000x
infilling material.
The guard hairs have a circular cross-section at the bottom, and an
ellipsoidal or flat-shaped outline in the middle and upper parts, of the hair
shaft. The diameter of these fibres is in the range of 50 to 120 µm. The
cuticular scales are either even tile-like or rounded tile-like in shape and
the scale surface is smooth with straight margins.
|
|
 Sciurus vulgaris
Sciurus vulgaris
----------------
English: Squirrel
German: Eichhorn
French: Ecureuil
Spanish: Ardilla
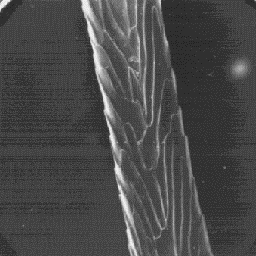
The medulla is wide, longitudinally
unbroken and situated symmetrically in the
central axial part of the hair shaft. The
overall medullar structure belongs to the
lattice type with a sheet-like infilling
material.
The cuticular structure
of an intermediate hair, 600x
|
|
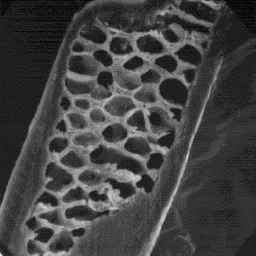 Sciurus vulgaris
Sciurus vulgaris
----------------
English: Squirrel
German: Eichhorn
French: Ecureuil
Spanish: Ardilla
Transverse section
of a guard hair, 600x
Numerical code for squirrel skin structure
------------------------------------------
Surface of the skin: 3-4-1
Fine fur fibres: 7.1-5.9-1-1-2-1-1-1-6.8-8.15-5.18
Intermediate fibres: 2.1-6-1-1-2-1-1-1-6.8-25.51-10.21
Guard hairs: 3.2-2.3-1-1-2-1-1-8-1-50.121-12.21
|




